Cities along the Silk Road
This article needs additional citations for verification. (November 2024) |
This article possibly contains original research. (June 2017) |
The Silk Road was an ancient network of trade routes that connected many communities of Eurasia by land and sea, stretching from the Mediterranean basin in the west to the Korean peninsula and the Japanese archipelago in the east.
Its main eastern end was in the Chinese city of Chang'an (modern-day Xi'an, China) and its main western end was in the Greek city of Antioch (modern-day Antakya, Turkey). It came into existence in the 2nd century BCE, when Emperor Wu of the Han dynasty was in power, and lasted until the 15th century CE, when the Ottoman Empire closed off the trade routes with Europe after it captured Constantinople and thereby conquered the Byzantine Empire.[1]
This article lists the cities along the Silk Road, sorted by region and the modern-day countries in which they lie.
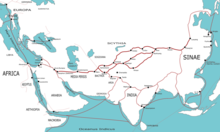
Terrestrial/land routes through Eurasia
[edit]Major cities, broadly from the Eastern Mediterranean to South Asia, and arranged roughly west to east in each area.
West Asia
[edit]Turkey
[edit]- Constantinople, ancient Byzantium (now Istanbul)
- Bursa
- Beypazarı
- Mudurnu
- Taraklı
- Konya
- Adana
- Antioch
- İzmir
- Trabzon
Azerbaijan
[edit]Georgia
[edit]Armenia
[edit]Lebanon
[edit]Syria
[edit]Iraq
[edit]Iran
[edit]- Tabriz
- Zanjan
- Rasht
- Kermanshah
- Hamadan
- Rey (or Ray in modern-day Tehran)
- Hecatompylos (Damghan)
- Sabzevar
- Nishapur
- Mashhad
- Tus
- Bam
- Yazd
- Qazvin
- Qumis (Hekatompylos)
Central Asia
[edit]Turkmenistan
[edit]- Nisa
- Merv
- Urgench

Ruins of Muhammad II's palace in Old Urgench. - Amul
Uzbekistan
[edit]Tajikistan
[edit]Kazakhstan
[edit]- Otrar
- Ispidjab (or Sairum)
- Taraz
- Hazrat-e Turkestan
The Mausoleum of Khoja Ahmed Yasavi in the town of Hazrat-e Turkestan. Built by Timur in the 1390s. - Almaty
Kyrgyzstan
[edit]South Asia
[edit]Afghanistan
[edit]Pakistan
[edit]India
[edit]- Tamralipta (or Tamluk)
- Leh
- Jaisalmer
- Mathura
- Varanasi (or Benares)
- Pataliputra
Nepal
[edit]Bangladesh
[edit]- Wari-Bateshwar
- Pundranagara
- Vikrampura
- Somapura
- Bhitargarh
- Sonargaon
- Chattagram/Chatgaon/Chittagong
- Comilla/Mainamati/Samatata
- Jahangir Nagar/Dhaka
Bhutan
[edit]
East Asia
[edit]China: the northern route along the Taklamakan Desert
[edit]
- Kashgar (or Kashi) (Major City)
- Liqian
- Aksu
- Kucha
- Korla
- Loulan
- Karasahr (Yanqi)
- Turpan (Turfan)
- Gaochang
- Chang'an
- Kumul/Hami
- Ürümqi
- Yumen Pass (or Jade Gate or Pass of the Jade Gate) (city called Yumenguan or Hecang)
- Anxi
China: the southern route along the Taklamakan Desert
[edit]- Kashgar (or Kashi) (Major City)
- Pishan
- Khotan
- Niya
- Mingfeng
- Endere
- Charchan
- Waxxari
- Ruoqiang Town (Charklik)
- Miran
- Yangguan, or Yangguan Pass
- Dunhuang
- the Mogao Caves
- Anxi
China: from Anxi/Dunhuang to Chang'an (Xi'an)
[edit]
- Dunhuang (Major City)
- Jiayuguan
- Jiuquan
- Zhangye
- Shandan
- Liangzhou (Wuwei)
- Tianzhu, Gansu
- Lanzhou
- Tianshui
- Baoji
- Chang'an (modern-day Xi'an)
Maritime routes to or along the Indian Ocean
[edit]South Asia
[edit]Pakistan
[edit]China
[edit]Bangladesh
[edit]Sri Lanka
[edit]- Colombo, Sri Lanka
India
[edit]- Tamralipta, West Bengal, India
- Poompuhar, Tamil Nadu, India
- Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
- Korkai, Tamil Nadu, India
- Muziris, Kerala, India
- Goa, India
- Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
- Cochin, Kerala, India
- Masulipatnam, Andhra Pradesh, India
- Lothal, Gujarat, India
Southern and Eastern Europe
[edit]Ukraine
[edit]- Sudak, Ukraine
Russia
[edit]Italy
[edit]West Asia
[edit]Oman
[edit]- Muscat, Oman
Yemen
[edit]- Aden, Yemen
Turkey
[edit]- Ayas, Turkey
Northeast Africa
[edit]Somalia
[edit]- Bosaso, Somalia
Egypt
[edit]- Suez, Egypt
Southeast Asia
[edit]Indonesia
[edit]- Perlak, Indonesia
Malaysia
[edit]- Kedah (Early history of Kedah)
- Malacca
Philippines
[edit]Thailand
[edit]Vietnam
[edit]List by Claudius Ptolemy
[edit]This following list is attributed to Ptolemy. All city names are Ptolemy's, throughout all his works. Most of the names are included in Geographia.
Some of the cities provided by Ptolemy either: no longer exist today or have moved to different locations. Nevertheless, Ptolemy has provided an important historical reference for researchers.
(This list has been alphabetized.)
- Africa
- East Africa – Akhmim, Aromaton Emporion, Axum, Coloe, Dongola, Juba, Maji, Opone, Panopolis, Sarapion, Sennar.
- North Africa – Caesarea, Carthage, Cyrene, Leptis Magna, Murzuk, Sijilmassa, Tamanrasset, Tingis.
- Arabia – Cane, Eudaemon Arabia, Mocha, Mosylon, Sanaʽa, Zafār (Saphar), Saue.
- Bangladesh – Sounagaora.
- China – Cattigara, Chengdu, Kaifeng, Kitai, Kunming, Yarkand.
- Europe – Aquileia, Athens, Augusta Treverorum (Trier), Gades (Cadiz), Ostia.
- India – Argaru, Astakapra, Bacare, Balita, Barake, Byzantion, Colchi, Erannoboas, Horaia, Kalliena, Mandagora, Melizeigara, Muziris, korkai, Poompuhar, Naura, Nelcynda, Paethana (Paithan), Palaepatmae, Palaesimundu, Poduca, Semylla, Sopatma, Suppara (Nalasopara), Tagara, Tymdis.
- Pakistan – Barbaricum, Peshawer, Taxilla
- Persia – Alexandria Areion, Kandahar, Persepolis.
- Persian Gulf – Apologos, Asabon, Charax, Gerrha (or Gerra), Ommana.
- Red Sea – Adulis, Aualites, Berenica, Malao, ancient Berbera, Muza, Myos Hormos, Ocalis, Ptolemais Theron.
- Southeast Asia – Kattigara (Oc Eo), Thaton, Trang.
- Unknown – Ecbatana (located in either modern Iran or Syria), Jiaohei.
See also
[edit]- Silk Roads: the Routes Network of Chang'an-Tianshan Corridor
- Silk Road transmission of Buddhism
- Silk Road transmission of art
- Silk Road numismatics
References
[edit]- ^ Garraty, John A. and Peter Gay, eds. The Columbia History of the World. New York: Dorset Press by arrangement with Harper & Row, 1981. ISBN 978-0-88029-004-3. Originally published New York: Harper & Row, 1972. p. 129.


